数据库结构
/* Redis database representation. There are multiple databases identified
* by integers from 0 (the default database) up to the max configured
* database. The database number is the 'id' field in the structure. */
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
unsigned long expires_cursor; /* Cursor of the active expire cycle. */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;
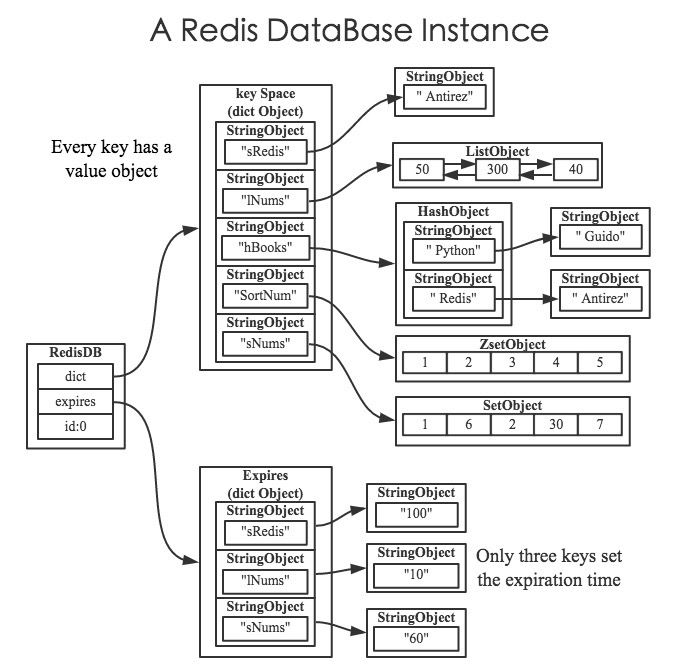
之前的list中有涉及ready_keys和watched_keys,watched_keys在事务一节中去分析。这里讨论键空间、键过期时间和数据库编码这三个参数。
吧。
数据库切换:
int selectDb(client *c, int id) {
if (id < 0 || id >= server.dbnum)
return C_ERR;
c->db = &server.db[id];
return C_OK;
}
键操作
/* Db->dict, keys are sds strings, vals are Redis objects. */
dictType dbDictType = {
dictSdsHash, /* hash function */
NULL, /* key dup */
NULL, /* val dup */
dictSdsKeyCompare, /* key compare */
dictSdsDestructor, /* key destructor */
dictObjectDestructor, /* val destructor */
dictExpandAllowed /* allow to expand */
};
在server.c的初始化,初始化了键空间
for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
server.db[j].dict = dictCreate(&dbDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].expires = dictCreate(&dbExpiresDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].expires_cursor = 0;
server.db[j].blocking_keys = dictCreate(&keylistDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].ready_keys = dictCreate(&objectKeyPointerValueDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].watched_keys = dictCreate(&keylistDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].id = j;
server.db[j].avg_ttl = 0;
server.db[j].defrag_later = listCreate();
listSetFreeMethod(server.db[j].defrag_later,(void (*)(void*))sdsfree);
}
查找键值对
/* Low level key lookup API, not actually called directly from commands
* implementations that should instead rely on lookupKeyRead(),
* lookupKeyWrite() and lookupKeyReadWithFlags(). */
robj *lookupKey(redisDb *db, robj *key, int flags) {
dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
/* Update the access time for the ageing algorithm.
* Don't do it if we have a saving child, as this will trigger
* a copy on write madness. */
if (!hasActiveChildProcess() && !(flags & LOOKUP_NOTOUCH)){
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
updateLFU(val);
} else {
val->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
}
}
return val;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
/* Return true if there are active children processes doing RDB saving,
* AOF rewriting, or some side process spawned by a loaded module. */
int hasActiveChildProcess() {
return server.child_pid != -1;
}
添加键值对
/* Add the key to the DB. It's up to the caller to increment the reference
* counter of the value if needed.
*
* The program is aborted if the key already exists. */
void dbAdd(redisDb *db, robj *key, robj *val) {
sds copy = sdsdup(key->ptr);
int retval = dictAdd(db->dict, copy, val);
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,retval == DICT_OK);
signalKeyAsReady(db, key, val->type);
if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyAdd(key->ptr);
}
修改键值对
/* Common case for genericSetKey() where the TTL is not retained. */
void setKey(client *c, redisDb *db, robj *key, robj *val) {
genericSetKey(c,db,key,val,0,1);
}
/* High level Set operation. This function can be used in order to set
* a key, whatever it was existing or not, to a new object.
*
* 1) The ref count of the value object is incremented.
* 2) clients WATCHing for the destination key notified.
* 3) The expire time of the key is reset (the key is made persistent),
* unless 'keepttl' is true.
*
* All the new keys in the database should be created via this interface.
* The client 'c' argument may be set to NULL if the operation is performed
* in a context where there is no clear client performing the operation. */
void genericSetKey(client *c, redisDb *db, robj *key, robj *val, int keepttl, int signal) {
if (lookupKeyWrite(db,key) == NULL) {
dbAdd(db,key,val);
} else {
dbOverwrite(db,key,val);
}
incrRefCount(val);
if (!keepttl) removeExpire(db,key);
if (signal) signalModifiedKey(c,db,key);
}
删除键值对
/* This is a wrapper whose behavior depends on the Redis lazy free
* configuration. Deletes the key synchronously or asynchronously. */
int dbDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
return server.lazyfree_lazy_server_del ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :
dbSyncDelete(db,key);
}
/* Delete a key, value, and associated expiration entry if any, from the DB.
* If there are enough allocations to free the value object may be put into
* a lazy free list instead of being freed synchronously. The lazy free list
* will be reclaimed in a different bio.c thread. */
//如果有足够的空间,value会被放进一个lazy free list而不是马上被删除。lazy free list会在其他的bio的线程中被回收
#define LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD 64
int dbAsyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
/* Deleting an entry from the expires dict will not free the sds of
* the key, because it is shared with the main dictionary. */
//如果在expires中也有,就先删除
if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0) dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr);
/* If the value is composed of a few allocations, to free in a lazy way
* is actually just slower... So under a certain limit we just free
* the object synchronously. */
//如果值是由几个内存块组成,用lazy的方式去释放会更慢,所以在一定限度下我就就同步free就行
dictEntry *de = dictUnlink(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
/* Tells the module that the key has been unlinked from the database. */
moduleNotifyKeyUnlink(key,val);
size_t free_effort = lazyfreeGetFreeEffort(key,val);
/* If releasing the object is too much work, do it in the background
* by adding the object to the lazy free list.
* Note that if the object is shared, to reclaim it now it is not
* possible. This rarely happens, however sometimes the implementation
* of parts of the Redis core may call incrRefCount() to protect
* objects, and then call dbDelete(). In this case we'll fall
* through and reach the dictFreeUnlinkedEntry() call, that will be
* equivalent to just calling decrRefCount(). */
if (free_effort > LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD && val->refcount == 1) {
atomicIncr(lazyfree_objects,1);
bioCreateLazyFreeJob(lazyfreeFreeObject,1, val);
dictSetVal(db->dict,de,NULL);
}
}
/* Release the key-val pair, or just the key if we set the val
* field to NULL in order to lazy free it later. */
if (de) {
dictFreeUnlinkedEntry(db->dict,de);
if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyDel(key->ptr);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
dictEntry *dictUnlink(dict *ht, const void *key) {
return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,1);
}
/* Search and remove an element. This is an helper function for
* dictDelete() and dictUnlink(), please check the top comment
* of those functions. */
static dictEntry *dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree) {
uint64_t h, idx;
dictEntry *he, *prevHe;
int table;
if (d->ht[0].used == 0 && d->ht[1].used == 0) return NULL;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
prevHe = NULL;
while(he) {
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) {
/* Unlink the element from the list */
if (prevHe)
prevHe->next = he->next;
else
d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next;
if (!nofree) {
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
zfree(he);
}
d->ht[table].used--;
return he;
}
prevHe = he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return NULL; /* not found */
}
lazyfree的会单独拿出来讲
/* Delete a key, value, and associated expiration entry if any, from the DB */
int dbSyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
/* Deleting an entry from the expires dict will not free the sds of
* the key, because it is shared with the main dictionary. */
if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0) dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr);
dictEntry *de = dictUnlink(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
/* Tells the module that the key has been unlinked from the database. */
moduleNotifyKeyUnlink(key,val);
dictFreeUnlinkedEntry(db->dict,de);
if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyDel(key->ptr);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
数据库的键过期操作
expires指针就指向一个字典结构,该字典存放着每个键及其对应的过期时间,与键空间一样,expires字典的键是字符串对象。Redis同样为其声明了一个特定的字典结构,由于过期时间为一个整数,因此其值释放函数可以不设定。
/* Keylist hash table type has unencoded redis objects as keys and
* lists as values. It's used for blocking operations (BLPOP) and to
* map swapped keys to a list of clients waiting for this keys to be loaded. */
dictType keylistDictType = {
dictObjHash, /* hash function */
NULL, /* key dup */
NULL, /* val dup */
dictObjKeyCompare, /* key compare */
dictObjectDestructor, /* key destructor */
dictListDestructor, /* val destructor */
NULL /* allow to expand */
};
设定键过期时间
#define dictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry, _val_) \
do { (entry)->v.s64 = _val_; } while(0)
/* Set an expire to the specified key. If the expire is set in the context
* of an user calling a command 'c' is the client, otherwise 'c' is set
* to NULL. The 'when' parameter is the absolute unix time in milliseconds
* after which the key will no longer be considered valid. */
void setExpire(client *c, redisDb *db, robj *key, long long when) {
dictEntry *kde, *de;
/* Reuse the sds from the main dict in the expire dict */
kde = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr);
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,kde != NULL);
de = dictAddOrFind(db->expires,dictGetKey(kde));
dictSetSignedIntegerVal(de,when);
int writable_slave = server.masterhost && server.repl_slave_ro == 0;
if (c && writable_slave && !(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER))
rememberSlaveKeyWithExpire(db,key);
}
获取键过期时间
/* Return the expire time of the specified key, or -1 if no expire
* is associated with this key (i.e. the key is non volatile) */
long long getExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
dictEntry *de;
/* No expire? return ASAP */
if (dictSize(db->expires) == 0 ||
(de = dictFind(db->expires,key->ptr)) == NULL) return -1;
/* The entry was found in the expire dict, this means it should also
* be present in the main dict (safety check). */
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr) != NULL);
return dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
}
删除键过期时间
int removeExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
/* An expire may only be removed if there is a corresponding entry in the
* main dict. Otherwise, the key will never be freed. */
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr) != NULL);
return dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr) == DICT_OK;
}
过期键删除策略
惰性删除与定期删除
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
if (!keyIsExpired(db,key)) return 0;
/* If we are running in the context of a slave, instead of
* evicting the expired key from the database, we return ASAP:
* the slave key expiration is controlled by the master that will
* send us synthesized DEL operations for expired keys.
*
* Still we try to return the right information to the caller,
* that is, 0 if we think the key should be still valid, 1 if
* we think the key is expired at this time. */
if (server.masterhost != NULL) return 1;
/* If clients are paused, we keep the current dataset constant,
* but return to the client what we believe is the right state. Typically,
* at the end of the pause we will properly expire the key OR we will
* have failed over and the new primary will send us the expire. */
if (checkClientPauseTimeoutAndReturnIfPaused()) return 1;
/* Delete the key */
deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagate(db,key);
return 1;
}
/* Delete the specified expired key and propagate expire. */
void deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagate(redisDb *db, robj *keyobj) {
mstime_t expire_latency;
latencyStartMonitor(expire_latency);
if (server.lazyfree_lazy_expire)
dbAsyncDelete(db,keyobj);
else
dbSyncDelete(db,keyobj);
latencyEndMonitor(expire_latency);
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("expire-del",expire_latency);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,"expired",keyobj,db->id);
signalModifiedKey(NULL, db, keyobj);
propagateExpire(db,keyobj,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
}
定期删除策略
Redis定义了一个例行处理程序serverCron,该程序每隔100ms执行一次,在其执行过程中会调用databasesCron函数,这个函数里面才会调用真正的定期删除函数activeExpireCycle。该函数每次执行时遍历指定个数的数据库,然后从expires字典中随机取出一个带过期时间的键,检查它是否过期,如过期直接删除。
每隔100处理数据库的个数由CRON_DBS_PER_CALL参数决定,该参数的默认值如下:
#define CRON_DBS_PER_CALL 16 // 每次处理16个数据库
/* Helper function for the activeExpireCycle() function.
* This function will try to expire the key that is stored in the hash table
* entry 'de' of the 'expires' hash table of a Redis database.
*
* If the key is found to be expired, it is removed from the database and
* 1 is returned. Otherwise no operation is performed and 0 is returned.
*
* When a key is expired, server.stat_expiredkeys is incremented.
*
* The parameter 'now' is the current time in milliseconds as is passed
* to the function to avoid too many gettimeofday() syscalls. */
int activeExpireCycleTryExpire(redisDb *db, dictEntry *de, long long now) {
long long t = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
if (now > t) {
sds key = dictGetKey(de);
robj *keyobj = createStringObject(key,sdslen(key));
// 将删除命令传播到AOF和附属节点
deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagate(db,keyobj);
decrRefCount(keyobj);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
