字典简介:
字典经常作为一种数据结构内置在很多高级编程语言中,C语言没有。因此Redis构建了自己的字典实现。Redis的数据库就是使用字典作为底层实现的,对数据库的增删改查都是建立在字典的操作上。此外字典还是redis中哈希键的底层实现。
数据结构:
redis定义了dictEntry,dictType,dictht和dict四个结构体来实现字典结构
dictEntry:哈希表节点
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next; //指向下一个哈希表节点,可以看出字典采用了开链法解决哈希冲突
} dictEntry;
union:C语言共用体,结构体和共用体的区别在于:结构体的各个成员会占用不同的内存,互相之间没有影响;而共用体的所有成员占用同一段内存,修改一个成员会影响其余所有成员。详见:
http://c.biancheng.net/view/2035.html
dictht:哈希表
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
**table:哈希表数组。指针数组
http://c.biancheng.net/cpp/html/3246.html
dict:字典
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
int16_t pauserehash; /* If >0 rehashing is paused (<0 indicates coding error) */
} dict;
dictType:字典类型函数
typedef struct dictType {
uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
内存示意图:
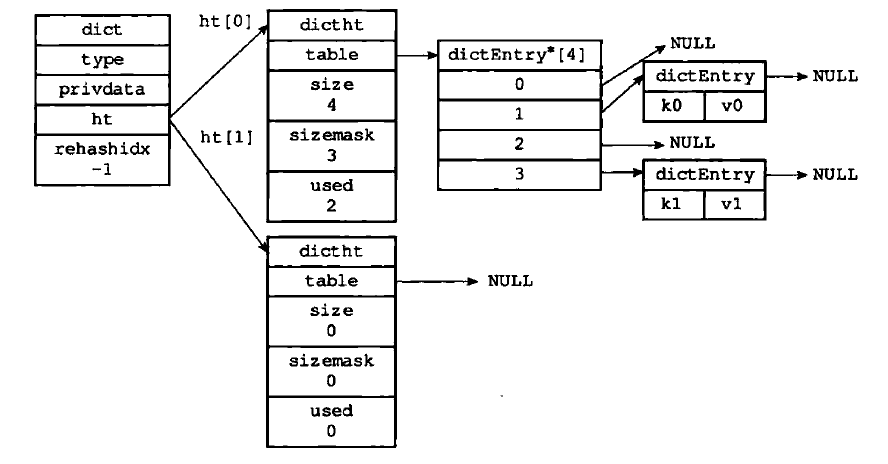
哈希算法:当往字典添加键值对时,需要根据键的大小计算出哈希值和索引值,然后再根据索引值,将包含新键值对的哈希表放到哈希表数组的指定索引上面。
/* Create a new hash table */
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d));
_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr);
return d;
}
/* Initialize the hash table */
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
_dictReset(&d->ht[0]);
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->type = type;
d->privdata = privDataPtr;
d->rehashidx = -1;
d->pauserehash = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
解决键冲突、渐进式rehash
#define dictIsRehashing(d) ((d)->rehashidx != -1)
/* This function performs just a step of rehashing, and only if hashing has
* not been paused for our hash table. When we have iterators in the
* middle of a rehashing we can't mess with the two hash tables otherwise
* some element can be missed or duplicated.
*
* This function is called by common lookup or update operations in the
* dictionary so that the hash table automatically migrates from H1 to H2
* while it is actively used. */
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
if (d->pauserehash == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0; //如果不在rehash就返回
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) { //如果这个table是空的,继续往下
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1; //如果到了最大rehash个数就返回
}
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
/* More to rehash... */
return 1;
}
dict的基本操作:
添加键值对:
如果没有进行rehash操作,计算出索引添加到ht[0]中 如果此刻正在进行rehash操作,根据ht[1]的参数计算出索引值添加到ht[1]中
/* Add an element to the target hash table */
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key,NULL);
if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Low level add or find:
* This function adds the entry but instead of setting a value returns the
* dictEntry structure to the user, that will make sure to fill the value
* field as they wish.
*
* This function is also directly exposed to the user API to be called
* mainly in order to store non-pointers inside the hash value, example:
*
* entry = dictAddRaw(dict,mykey,NULL);
* if (entry != NULL) dictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry,1000);
*
* Return values:
*
* If key already exists NULL is returned, and "*existing" is populated
* with the existing entry if existing is not NULL.
*
* If key was added, the hash entry is returned to be manipulated by the caller.
*/
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key, dictEntry **existing)
{
long index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d); //如果在rehash 就进行一次渐近式rehash
/* Get the index of the new element, or -1 if
* the element already exists. */
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key, dictHashKey(d,key), existing)) == -1)
return NULL;
/* Allocate the memory and store the new entry.
* Insert the element in top, with the assumption that in a database
* system it is more likely that recently added entries are accessed
* more frequently. */
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
entry->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = entry;
ht->used++;
/* Set the hash entry fields. */
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}
/* Returns the index of a free slot that can be populated with
* a hash entry for the given 'key'.
* If the key already exists, -1 is returned
* and the optional output parameter may be filled.
*
* Note that if we are in the process of rehashing the hash table, the
* index is always returned in the context of the second (new) hash table. */
static long _dictKeyIndex(dict *d, const void *key, uint64_t hash, dictEntry **existing)
{
unsigned long idx, table;
dictEntry *he;
if (existing) *existing = NULL;
/* Expand the hash table if needed */
if (_dictExpandIfNeeded(d) == DICT_ERR)
return -1;
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = hash & d->ht[table].sizemask;
/* Search if this slot does not already contain the given key */
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while(he) {
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) {
if (existing) *existing = he;
return -1;
}
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return idx;
}
替换值:
/* Add or Overwrite:
* Add an element, discarding the old value if the key already exists.
* Return 1 if the key was added from scratch, 0 if there was already an
* element with such key and dictReplace() just performed a value update
* operation. */
int dictReplace(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
dictEntry *entry, *existing, auxentry;
/* Try to add the element. If the key
* does not exists dictAdd will succeed. */
entry = dictAddRaw(d,key,&existing); // 若没有key的话先设置key
if (entry) {
dictSetVal(d, entry, val); //然后设置value
return 1;
}
/* Set the new value and free the old one. Note that it is important
* to do that in this order, as the value may just be exactly the same
* as the previous one. In this context, think to reference counting,
* you want to increment (set), and then decrement (free), and not the
* reverse. */
auxentry = *existing; //auxentry为原来的entry节点
dictSetVal(d, existing, val);
dictFreeVal(d, &auxentry);
return 0;
}
#define dictSetVal(d, entry, _val_) do { \
if ((d)->type->valDup) \
(entry)->v.val = (d)->type->valDup((d)->privdata, _val_); \
else \
(entry)->v.val = (_val_); \
} while(0)
#define dictSetKey(d, entry, _key_) do { \
if ((d)->type->keyDup) \
(entry)->key = (d)->type->keyDup((d)->privdata, _key_); \
else \
(entry)->key = (_key_); \
} while(0)
#define dictFreeKey(d, entry) \
if ((d)->type->keyDestructor) \
(d)->type->keyDestructor((d)->privdata, (entry)->key)
查找键值对:
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key)
{
dictEntry *he;
uint64_t h, idx, table;
if (dictSize(d) == 0) return NULL; /* dict is empty */
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while(he) {
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}
删除键值对:
int dictDelete(dict *ht, const void *key) {
return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,0) ? DICT_OK : DICT_ERR;
}
static dictEntry *dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree) {
uint64_t h, idx;
dictEntry *he, *prevHe;
int table;
if (d->ht[0].used == 0 && d->ht[1].used == 0) return NULL;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
prevHe = NULL;
while(he) {
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) {
/* Unlink the element from the list */
if (prevHe)
prevHe->next = he->next;
else
d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next;
if (!nofree) {
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
zfree(he);
}
d->ht[table].used--;
return he;
}
prevHe = he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return NULL; /* not found */
}
字典删除:
/* Clear & Release the hash table */
void dictRelease(dict *d)
{
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[0],NULL);
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[1],NULL);
zfree(d);
}
/* Destroy an entire dictionary */
int _dictClear(dict *d, dictht *ht, void(callback)(void *)) {
unsigned long i;
/* Free all the elements */
for (i = 0; i < ht->size && ht->used > 0; i++) {
dictEntry *he, *nextHe;
if (callback && (i & 65535) == 0) callback(d->privdata);
if ((he = ht->table[i]) == NULL) continue;
while(he) {
nextHe = he->next;
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
zfree(he);
ht->used--;
he = nextHe;
}
}
/* Free the table and the allocated cache structure */
zfree(ht->table);
/* Re-initialize the table */
_dictReset(ht);
return DICT_OK; /* never fails */
}
小结:
Redis字典结构采用哈希表作为底层实现,每个字典包括两个哈希表,一个用来平常使用,另一个在rehash的时候使用。Redis提供了三种哈希算法,对整数,字符串等类型的键都能较好的处理。Redis的哈希表采用了链地址法来解决哈希冲突。最有特点的是,Redis在对字典进行扩容和收缩时,需要对哈希表中的所有键值对rehash到新哈希表里面,这个rehash操作不是一次性完成的,而是采用渐进式完成,这一措施使得rehash过程不会影响Redis对字典进行增删查改操作的效率。
