
复习下zpilist和hashtbale的数据结构:
ziplist

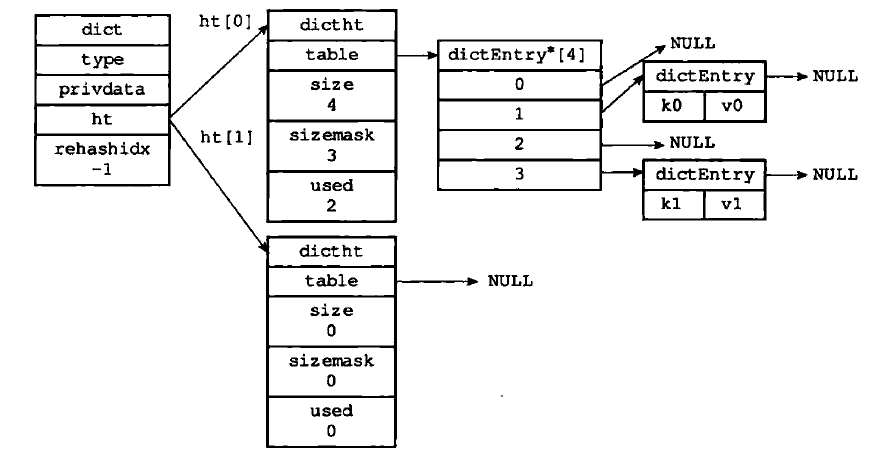
hashtable
robj数据结构:
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
int refcount;
void *ptr;
} robj;
其中type为hash的时候,encoding可能是ziplist或者hashtable,如果底层编码是ziplist的话,hash键按照如下方式排列,每一个key或value都作为ziplist的一个节点。
|ziplistHeader| entry1 | entry2 | entry3 | entry4 | end |
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
| key1 | value1 | key2 | value2 |
创建一个hash对象,默认是用ziplist
robj *createHashObject(void) {
unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew();
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_HASH, zl);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST;
return o;
}
但超过红线后底层实现就会变成hash,原因也是和intset类似,连续内存优缺点。
# Hashes are encoded using a memory efficient data structure when they have a
# small number of entries, and the biggest entry does not exceed a given
# threshold. These thresholds can be configured using the following directives.
hash-max-ziplist-entries 512 //最多entry个数
hash-max-ziplist-value 64 //ziplist中最大能存放值的长度
hash的迭代器结构:
/* Structure to hold hash iteration abstraction. Note that iteration over
* hashes involves both fields and values. Because it is possible that
* not both are required, store pointers in the iterator to avoid
* unnecessary memory allocation for fields/values. */
typedef struct {
robj *subject;
int encoding;
unsigned char *fptr, *vptr;
dictIterator *di;
dictEntry *de;
} hashTypeIterator;
迭代器操作
hashTypeIterator *hashTypeInitIterator(robj *subject) {
hashTypeIterator *hi = zmalloc(sizeof(hashTypeIterator));
hi->subject = subject;
hi->encoding = subject->encoding;
if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
hi->fptr = NULL;
hi->vptr = NULL;
} else if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
hi->di = dictGetIterator(subject->ptr);
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");
}
return hi;
}
void hashTypeReleaseIterator(hashTypeIterator *hi) {
if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT)
dictReleaseIterator(hi->di);
zfree(hi);
}
/* Move to the next entry in the hash. Return C_OK when the next entry
* could be found and C_ERR when the iterator reaches the end. */
int hashTypeNext(hashTypeIterator *hi) {
if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
unsigned char *zl;
unsigned char *fptr, *vptr;
zl = hi->subject->ptr;
fptr = hi->fptr;
vptr = hi->vptr;
if (fptr == NULL) {
/* Initialize cursor */
serverAssert(vptr == NULL);
fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, 0);
} else {
/* Advance cursor */
serverAssert(vptr != NULL);
fptr = ziplistNext(zl, vptr);
}
if (fptr == NULL) return C_ERR;
/* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */
vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr);
serverAssert(vptr != NULL);
/* fptr, vptr now point to the first or next pair */
hi->fptr = fptr;
hi->vptr = vptr;
} else if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
if ((hi->de = dictNext(hi->di)) == NULL) return C_ERR;
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");
}
return C_OK;
}
实现比较简单,需要注意下ziplist的value和key相互交替安插。
/* Add a new field, overwrite the old with the new value if it already exists.
* Return 0 on insert and 1 on update.
*
* By default, the key and value SDS strings are copied if needed, so the
* caller retains ownership of the strings passed. However this behavior
* can be effected by passing appropriate flags (possibly bitwise OR-ed):
*默认情况下我们支持对键值的sds的复制以让调用者保留传递的字符串的所有权,但这个功能可以被传入的flag的参数影响。
* HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD -- The SDS field ownership passes to the function.
* HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE -- The SDS value ownership passes to the function.
*
* When the flags are used the caller does not need to release the passed
* SDS string(s). It's up to the function to use the string to create a new
* entry or to free the SDS string before returning to the caller.
*当这个flag被使用的时候,调用者无需释放传递来的sds字符串。这个取决于function去使用字符串去创建一个新的entry或者释放sds在返回调用者之前
* HASH_SET_COPY corresponds to no flags passed, and means the default
* semantics of copying the values if needed.
*
*/
#define ZIPLIST_HEAD 0
#define ZIPLIST_TAIL 1
#define HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD (1<<0)
#define HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE (1<<1)
#define HASH_SET_COPY 0
int hashTypeSet(robj *o, sds field, sds value, int flags) {
int update = 0;
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
unsigned char *zl, *fptr, *vptr;
zl = o->ptr;
fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, ZIPLIST_HEAD); //找到第一个entry
if (fptr != NULL) {
fptr = ziplistFind(zl, fptr, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field), 1);
if (fptr != NULL) { //找到了就替换
/* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */
vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr);
serverAssert(vptr != NULL);
update = 1;
/* Replace value */
zl = ziplistReplace(zl, vptr, (unsigned char*)value,
sdslen(value));
}
}
if (!update) { //没找到就放在最后面
/* Push new field/value pair onto the tail of the ziplist */
zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field),
ZIPLIST_TAIL);
zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)value, sdslen(value),
ZIPLIST_TAIL);
}
o->ptr = zl;
/* Check if the ziplist needs to be converted to a hash table */
if (hashTypeLength(o) > server.hash_max_ziplist_entries) //插入的话判断是否需要转换为hash
hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
} else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
dictEntry *de = dictFind(o->ptr,field);
if (de) { // 找到的话就先释放
sdsfree(dictGetVal(de));
if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) {
dictGetVal(de) = value; //直接把值附上去
value = NULL;
} else {
dictGetVal(de) = sdsdup(value); //复制值再附上去
}
update = 1;
} else { //没找到就新增
sds f,v;
if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD) {
f = field;
field = NULL;
} else {
f = sdsdup(field);
}
if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) {
v = value;
value = NULL;
} else {
v = sdsdup(value);
}
dictAdd(o->ptr,f,v);
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");
}
/* Free SDS strings we did not referenced elsewhere if the flags
* want this function to be responsible. */
if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD && field) sdsfree(field);
if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE && value) sdsfree(value);
return update;
}
/* Returns an offset to use for iterating with ziplistNext. When the given
* index is negative, the list is traversed back to front. When the list
* doesn't contain an element at the provided index, NULL is returned. */
/*返回用于与ziplistNext迭代的偏移量。当给定的
*索引为负数,列表将从后到前遍历。当名单
*在提供的索引中不包含元素,返回NULL。*/
unsigned char *ziplistIndex(unsigned char *zl, int index) {
unsigned char *p;
unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0;
if (index < 0) { //从后向前遍历
index = (-index)-1;
p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl); //找到最后一个entry
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) { //有元素
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen); //获得该entry的prevlensize, prevlen
while (prevlen > 0 && index--) { //如果prevlen有值并且index--也大于0
p -= prevlen;
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen); //往前找
}
}
} else {
p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl); //正的就从前面找
while (p[0] != ZIP_END && index--) {
p += zipRawEntryLength(p);
}
}
return (p[0] == ZIP_END || index > 0) ? NULL : p;
}
/* Find pointer to the entry equal to the specified entry. Skip 'skip' entries
* between every comparison. Returns NULL when the field could not be found. */
找到entry和指定entry相同的指针,跳过‘skip’个entry在每一个比较之间。返回空如果没找到的话
unsigned char *ziplistFind(unsigned char *p, unsigned char *vstr, unsigned int vlen, unsigned int skip) {
int skipcnt = 0;
unsigned char vencoding = 0;
long long vll = 0;
while (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
unsigned int prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len;
unsigned char *q;
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize); //获取p的size占的长度
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len); lensize获得entry需要保存长度的size,len表示entry的长度
q = p + prevlensize + lensize;
if (skipcnt == 0) {
/* Compare current entry with specified entry */
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {
if (len == vlen && memcmp(q, vstr, vlen) == 0) {
return p;
}
} else {
/* Find out if the searched field can be encoded. Note that
* we do it only the first time, once done vencoding is set
* to non-zero and vll is set to the integer value. */
if (vencoding == 0) {
if (!zipTryEncoding(vstr, vlen, &vll, &vencoding)) {
/* If the entry can't be encoded we set it to
* UCHAR_MAX so that we don't retry again the next
* time. */
vencoding = UCHAR_MAX;
}
/* Must be non-zero by now */
assert(vencoding);
}
/* Compare current entry with specified entry, do it only
* if vencoding != UCHAR_MAX because if there is no encoding
* possible for the field it can't be a valid integer. */
if (vencoding != UCHAR_MAX) {
long long ll = zipLoadInteger(q, encoding);
if (ll == vll) {
return p;
}
}
}
/* Reset skip count */
skipcnt = skip;
} else {
/* Skip entry */
skipcnt--;
}
/* Move to next entry */
p = q + len;
}
return NULL;
}
/* Check the length of a number of objects to see if we need to convert a
* ziplist to a real hash. Note that we only check string encoded objects
* as their string length can be queried in constant time. */
/*检查多个对象的长度,看看我们是否需要转换一个
*拉链列表到真正的哈希。请注意,我们只检查字符串编码的对象
*因为它们的字符串长度可以在恒定时间内查询。
void hashTypeTryConversion(robj *o, robj **argv, int start, int end) {
int i;
size_t sum = 0;
if (o->encoding != OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) return;
for (i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if (!sdsEncodedObject(argv[i]))
continue;
size_t len = sdslen(argv[i]->ptr);
if (len > server.hash_max_ziplist_value) {
hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
return;
}
sum += len;
}
if (!ziplistSafeToAdd(o->ptr, sum))
hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
}
void hashTypeConvert(robj *o, int enc) {
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
hashTypeConvertZiplist(o, enc);
} else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
serverPanic("Not implemented");
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");
}
}
void hashTypeConvertZiplist(robj *o, int enc) {
serverAssert(o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST);
if (enc == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
/* Nothing to do... */
} else if (enc == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
hashTypeIterator *hi;
dict *dict;
int ret;
hi = hashTypeInitIterator(o);
dict = dictCreate(&hashDictType, NULL);
while (hashTypeNext(hi) != C_ERR) {
sds key, value;
key = hashTypeCurrentObjectNewSds(hi,OBJ_HASH_KEY);
value = hashTypeCurrentObjectNewSds(hi,OBJ_HASH_VALUE);
ret = dictAdd(dict, key, value);
if (ret != DICT_OK) {
serverLogHexDump(LL_WARNING,"ziplist with dup elements dump",
o->ptr,ziplistBlobLen(o->ptr));
serverPanic("Ziplist corruption detected");
}
}
hashTypeReleaseIterator(hi);
zfree(o->ptr);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_HT;
o->ptr = dict;
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");
}
}
主要看下set和转换的代码,总体逻辑比较简单清晰。
