
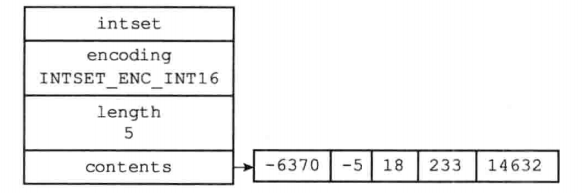
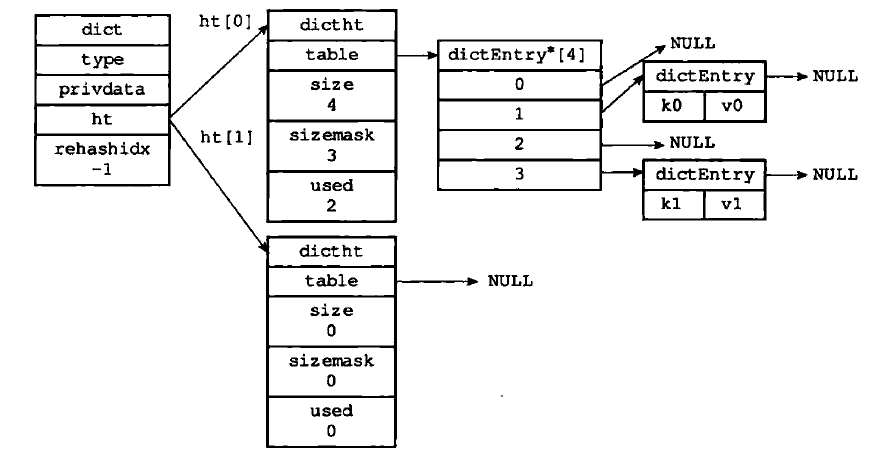
复习下intset和hashtbale的数据结构:
intset
hashtable
robj数据结构:
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
int refcount;
void *ptr;
} robj;
其中type为set的时候,encoding可能是intset或者hashtable
set的迭代器结构:
/* Structure to hold set iteration abstraction. */
typedef struct {
robj *subject;
int encoding;
int ii; /* intset iterator */ //intset的迭代器,就是下标
dictIterator *di; //hashtable使用的迭代器
} setTypeIterator;
迭代器操作
setTypeIterator *setTypeInitIterator(robj *subject) {
setTypeIterator *si = zmalloc(sizeof(setTypeIterator));
si->subject = subject;
si->encoding = subject->encoding;
if (si->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
si->di = dictGetIterator(subject->ptr);
} else if (si->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {
si->ii = 0;
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown set encoding");
}
return si;
}
void setTypeReleaseIterator(setTypeIterator *si) {
if (si->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT)
dictReleaseIterator(si->di);
zfree(si);
}
/* Move to the next entry in the set. Returns the object at the current
* position.
*
* Since set elements can be internally be stored as SDS strings or
* simple arrays of integers, setTypeNext returns the encoding of the
* set object you are iterating, and will populate the appropriate pointer
* (sdsele) or (llele) accordingly.
*
* Note that both the sdsele and llele pointers should be passed and cannot
* be NULL since the function will try to defensively populate the non
* used field with values which are easy to trap if misused.
*
* When there are no longer elements -1 is returned. */
int setTypeNext(setTypeIterator *si, sds *sdsele, int64_t *llele) {
if (si->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
dictEntry *de = dictNext(si->di);
if (de == NULL) return -1;
*sdsele = dictGetKey(de);
*llele = -123456789; /* Not needed. Defensive. */
} else if (si->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {
if (!intsetGet(si->subject->ptr,si->ii++,llele))
return -1;
*sdsele = NULL; /* Not needed. Defensive. */
} else {
serverPanic("Wrong set encoding in setTypeNext");
}
return si->encoding;
}
从迭代器的操作就可以看出来,因为set底层支持两种数据结构所以所有的方法都需要考虑两种情况。
创建set
void saddCommand(client *c) {
robj *set;
int j, added = 0;
set = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[1]);
if (set == NULL) {
set = setTypeCreate(c->argv[2]->ptr); //如果是空就新建一个,以第三个参数未值传
dbAdd(c->db,c->argv[1],set);
} else {
if (set->type != OBJ_SET) {
addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr);
return;
}
}
for (j = 2; j < c->argc; j++) { //添加新元素
if (setTypeAdd(set,c->argv[j]->ptr)) added++;
}
if (added) {
signalModifiedKey(c,c->db,c->argv[1]);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_SET,"sadd",c->argv[1],c->db->id);
}
server.dirty += added;
addReplyLongLong(c,added);
}
/* Factory method to return a set that *can* hold "value". When the object has
* an integer-encodable value, an intset will be returned. Otherwise a regular
* hash table. */
robj *setTypeCreate(sds value) {
if (isSdsRepresentableAsLongLong(value,NULL) == C_OK) //如果第三个参数可以是int就创建intset
return createIntsetObject();
return createSetObject();
}
robj *createIntsetObject(void) {
intset *is = intsetNew();
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_SET,is);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET;
return o;
}
robj *createSetObject(void) {
dict *d = dictCreate(&setDictType,NULL);
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_SET,d);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_HT;
return o;
}
添加
/* Add the specified value into a set.
*
* If the value was already member of the set, nothing is done and 0 is
* returned, otherwise the new element is added and 1 is returned. */
int setTypeAdd(robj *subject, sds value) {
long long llval;
if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
dict *ht = subject->ptr;
dictEntry *de = dictAddRaw(ht,value,NULL);
if (de) {
dictSetKey(ht,de,sdsdup(value));
dictSetVal(ht,de,NULL);
return 1;
}
} else if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {
if (isSdsRepresentableAsLongLong(value,&llval) == C_OK) {
uint8_t success = 0;
subject->ptr = intsetAdd(subject->ptr,llval,&success);
if (success) {
/* Convert to regular set when the intset contains
* too many entries. */
size_t max_entries = server.set_max_intset_entries;
/* limit to 1G entries due to intset internals. */
if (max_entries >= 1<<30) max_entries = 1<<30;
if (intsetLen(subject->ptr) > max_entries) //如果元素太多就转换
setTypeConvert(subject,OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
return 1;
}
} else {
/* Failed to get integer from object, convert to regular set. */
//如果新元素不能转换为int就转换
setTypeConvert(subject,OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
/* The set *was* an intset and this value is not integer
* encodable, so dictAdd should always work. */
serverAssert(dictAdd(subject->ptr,sdsdup(value),NULL) == DICT_OK);
return 1;
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown set encoding");
}
return 0;
}
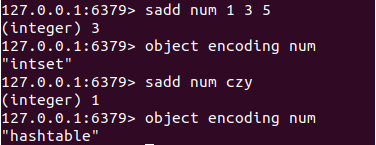
/* Convert the set to specified encoding. The resulting dict (when converting
* to a hash table) is presized to hold the number of elements in the original
* set. */
void setTypeConvert(robj *setobj, int enc) {
setTypeIterator *si;
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,setobj,setobj->type == OBJ_SET &&
setobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET);
if (enc == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
int64_t intele;
dict *d = dictCreate(&setDictType,NULL);
sds element;
/* Presize the dict to avoid rehashing */
dictExpand(d,intsetLen(setobj->ptr));
/* To add the elements we extract integers and create redis objects */
si = setTypeInitIterator(setobj);
while (setTypeNext(si,&element,&intele) != -1) {
element = sdsfromlonglong(intele);
serverAssert(dictAdd(d,element,NULL) == DICT_OK);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si);
setobj->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_HT;
zfree(setobj->ptr);
setobj->ptr = d;
} else {
serverPanic("Unsupported set conversion");
}
}
先创一个ht的set然后再从intset搬过来。
set还支持集合运算:如下图
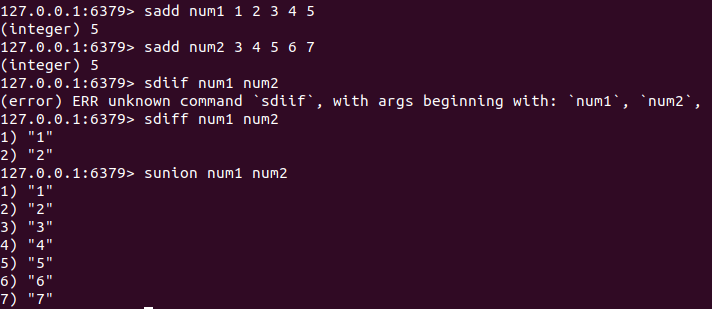
/* SUNION key [key ...] */
void sunionCommand(client *c) {
sunionDiffGenericCommand(c,c->argv+1,c->argc-1,NULL,SET_OP_UNION);
}
/* SDIFF key [key ...] */
void sdiffCommand(client *c) {
sunionDiffGenericCommand(c,c->argv+1,c->argc-1,NULL,SET_OP_DIFF);
}
void sunionDiffGenericCommand(client *c, robj **setkeys, int setnum,
robj *dstkey, int op) {
robj **sets = zmalloc(sizeof(robj*)*setnum);
setTypeIterator *si;
robj *dstset = NULL;
sds ele;
int j, cardinality = 0; //基数
int diff_algo = 1;
// 取出所有集合对象,并添加到集合数组中
for (j = 0; j < setnum; j++) {
robj *setobj = dstkey ?
lookupKeyWrite(c->db,setkeys[j]) :
lookupKeyRead(c->db,setkeys[j]);
if (!setobj) {
sets[j] = NULL;
continue;
}
if (checkType(c,setobj,OBJ_SET)) {
zfree(sets);
return;
}
sets[j] = setobj;
}
/* Select what DIFF algorithm to use.
*
* Algorithm 1 is O(N*M) where N is the size of the element first set
* and M the total number of sets.
*
* Algorithm 2 is O(N) where N is the total number of elements in all
* the sets.
*
* We compute what is the best bet with the current input here. */
// redis有两种不同的算法来进行diff计算,时间复杂度也给出来了
if (op == SET_OP_DIFF && sets[0]) {
long long algo_one_work = 0, algo_two_work = 0;
for (j = 0; j < setnum; j++) {
if (sets[j] == NULL) continue;
algo_one_work += setTypeSize(sets[0]);
algo_two_work += setTypeSize(sets[j]);
}
/* Algorithm 1 has better constant times and performs less operations
* if there are elements in common. Give it some advantage. */
algo_one_work /= 2;
diff_algo = (algo_one_work <= algo_two_work) ? 1 : 2;
if (diff_algo == 1 && setnum > 1) {
/* With algorithm 1 it is better to order the sets to subtract
* by decreasing size, so that we are more likely to find
* duplicated elements ASAP. */
//如果是算法一,最好先排序,有助于优化算法性能
qsort(sets+1,setnum-1,sizeof(robj*),
qsortCompareSetsByRevCardinality);
}
}
/* We need a temp set object to store our union. If the dstkey
* is not NULL (that is, we are inside an SUNIONSTORE operation) then
* this set object will be the resulting object to set into the target key*/
//使用一个临时集合保存结果集
dstset = createIntsetObject();
if (op == SET_OP_UNION) {
/* Union is trivial, just add every element of every set to the
* temporary set. */
for (j = 0; j < setnum; j++) {
if (!sets[j]) continue; /* non existing keys are like empty sets */
si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[j]);
while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {
if (setTypeAdd(dstset,ele)) cardinality++;
sdsfree(ele);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si);
}
} else if (op == SET_OP_DIFF && sets[0] && diff_algo == 1) {
/* DIFF Algorithm 1:
*
* We perform the diff by iterating all the elements of the first set,
* and only adding it to the target set if the element does not exist
* into all the other sets.
*
* This way we perform at max N*M operations, where N is the size of
* the first set, and M the number of sets. */
si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[0]);
//第一个集合和其他集合进行比较
while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {
for (j = 1; j < setnum; j++) {
if (!sets[j]) continue; /* no key is an empty set. */
if (sets[j] == sets[0]) break; /* same set! */
if (setTypeIsMember(sets[j],ele)) break;
}
if (j == setnum) {
/* There is no other set with this element. Add it. */
setTypeAdd(dstset,ele);
cardinality++;
}
sdsfree(ele);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si);
} else if (op == SET_OP_DIFF && sets[0] && diff_algo == 2) {
/* DIFF Algorithm 2:
*
* Add all the elements of the first set to the auxiliary set.
* Then remove all the elements of all the next sets from it.
*
* This is O(N) where N is the sum of all the elements in every
* set. */
//如果是集合零添加,非集合零去除
for (j = 0; j < setnum; j++) {
if (!sets[j]) continue; /* non existing keys are like empty sets */
si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[j]);
while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {
if (j == 0) {
if (setTypeAdd(dstset,ele)) cardinality++;
} else {
if (setTypeRemove(dstset,ele)) cardinality--;
}
sdsfree(ele);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si);
/* Exit if result set is empty as any additional removal
* of elements will have no effect. */
if (cardinality == 0) break;
}
}
/* Output the content of the resulting set, if not in STORE mode */
//输出结果集合
if (!dstkey) {
addReplySetLen(c,cardinality);
si = setTypeInitIterator(dstset);
while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {
addReplyBulkCBuffer(c,ele,sdslen(ele));
sdsfree(ele);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si);
server.lazyfree_lazy_server_del ? freeObjAsync(dstset) :
decrRefCount(dstset);
} else {
/* If we have a target key where to store the resulting set
* create this key with the result set inside */
//保存到数据库
int deleted = dbDelete(c->db,dstkey);
if (setTypeSize(dstset) > 0) {
dbAdd(c->db,dstkey,dstset);
addReplyLongLong(c,setTypeSize(dstset));
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_SET,
op == SET_OP_UNION ? "sunionstore" : "sdiffstore",
dstkey,c->db->id);
} else {
decrRefCount(dstset);
addReply(c,shared.czero);
if (deleted)
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",
dstkey,c->db->id);
}
signalModifiedKey(c,c->db,dstkey);
server.dirty++;
}
zfree(sets);
}
之前没注意的dictIterator。这里再分析一下
/* If safe is set to 1 this is a safe iterator, that means, you can call
* dictAdd, dictFind, and other functions against the dictionary even while
* iterating. Otherwise it is a non safe iterator, and only dictNext()
* should be called while iterating. */
// 如果safe是1的话,就是一个安全的迭代器,可以执行所有操作。如果不是的话就是能查询
typedef struct dictIterator {
dict *d;
long index;
int table, safe;
dictEntry *entry, *nextEntry;
/* unsafe iterator fingerprint for misuse detection. */
long long fingerprint;
} dictIterator;
void dictReleaseIterator(dictIterator *iter)
{
if (!(iter->index == -1 && iter->table == 0)) {
if (iter->safe) //如果是安全迭代器 直接删除
iter->d->iterators--;
else /*如果不是需要,判断迭代器的指纹和dict指纹一样,If the two fingerprints are different it means that the user of the iterator performed forbidden operations against the dictionary while iterating. */
assert(iter->fingerprint == dictFingerprint(iter->d));
}
zfree(iter);
}
总结:intset唯一优点就是节省内存,因为它是连续内存的,所以效率方面是比不上hashtable的,数目过多导致内存过大更加剧了性能的劣势,所以需要转换成hashtable。
